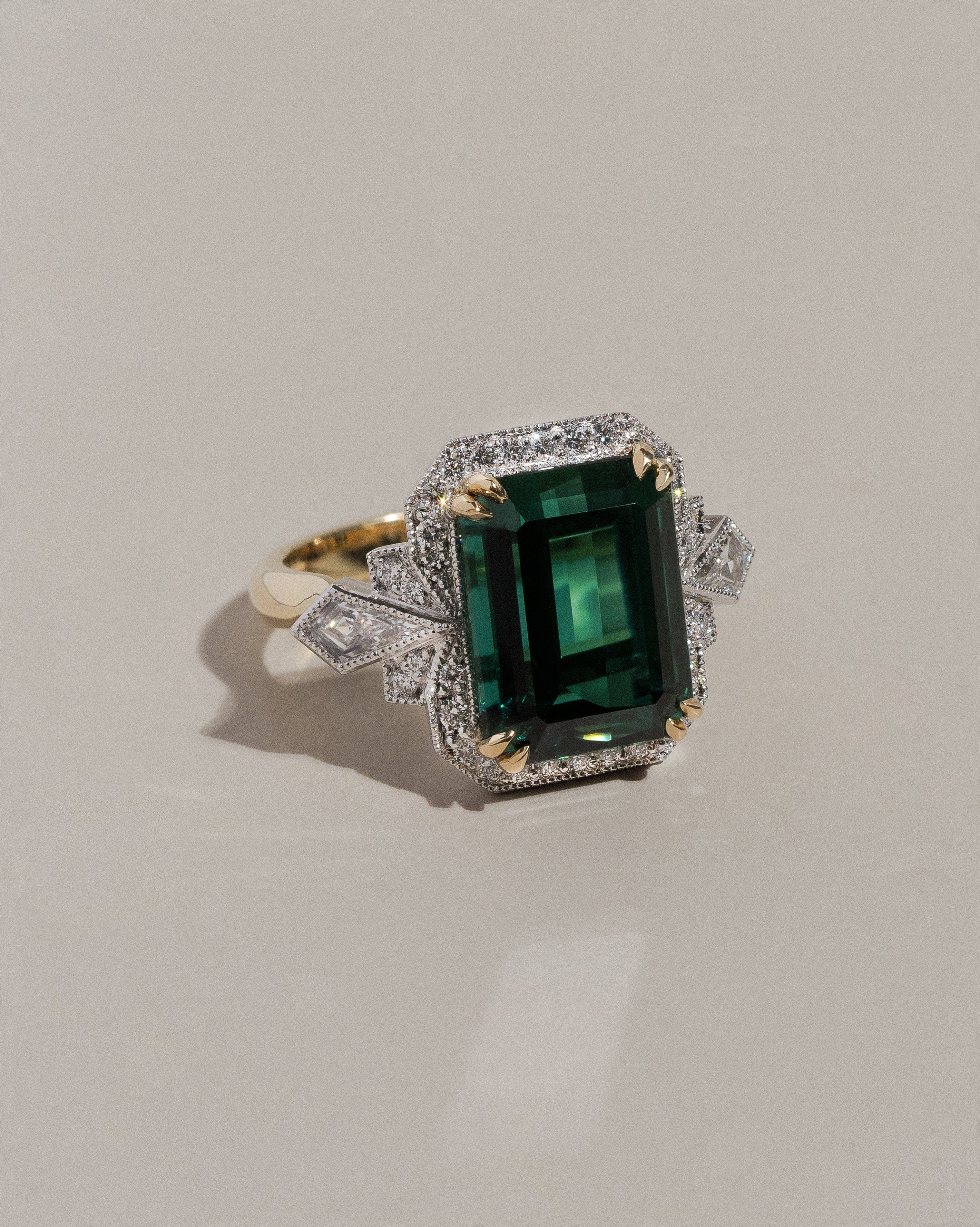
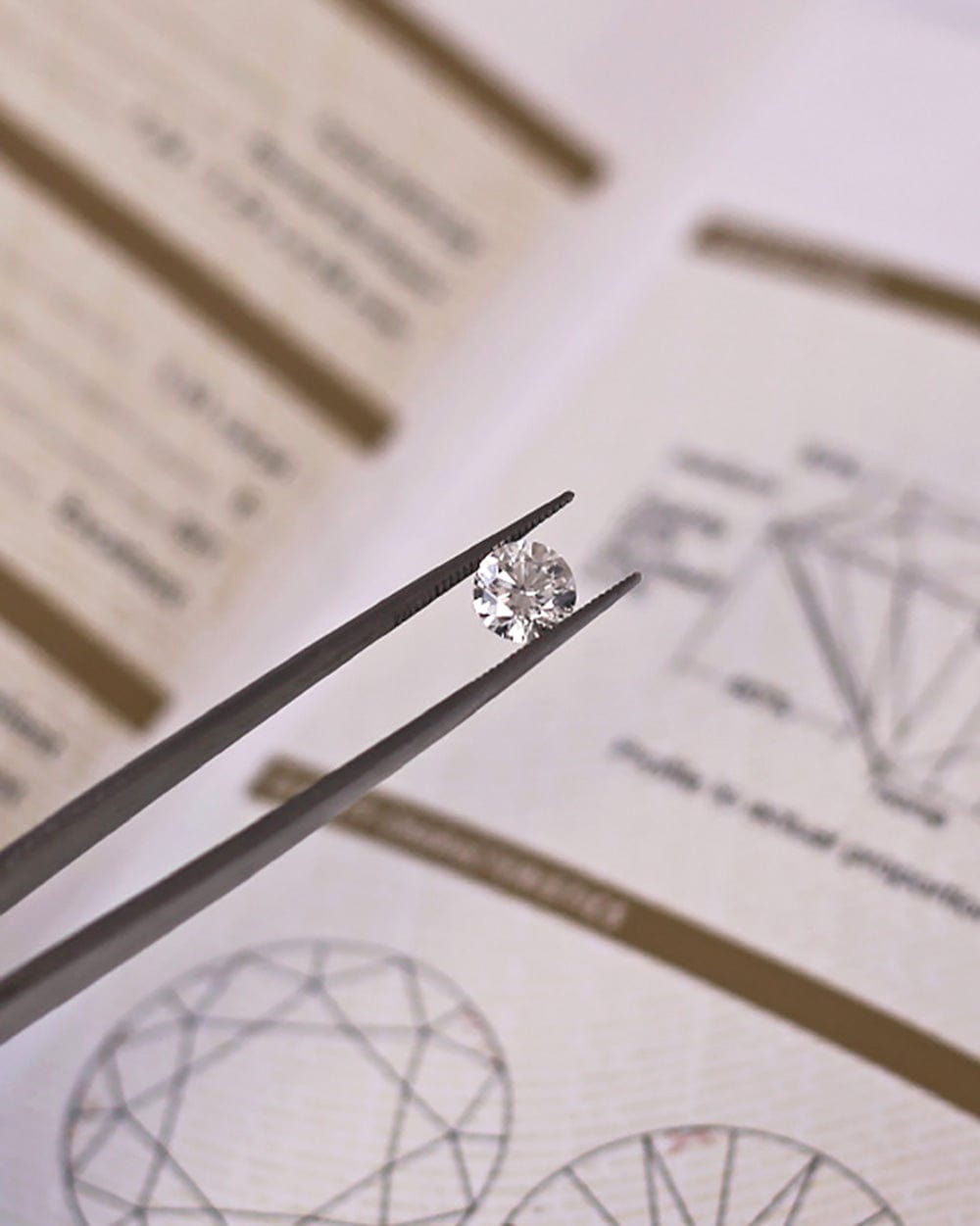
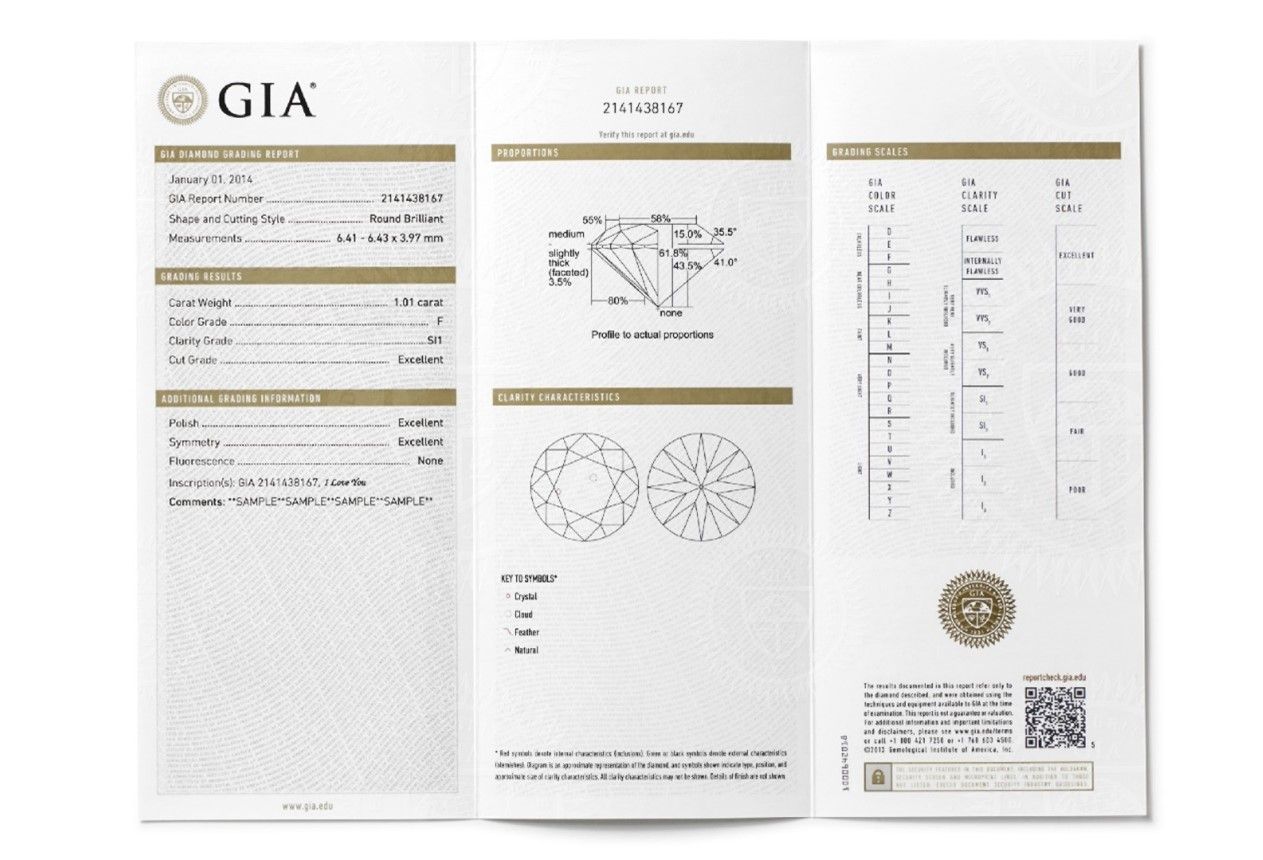
Investing in a diamond or an engagement ring can be a daunting task, but when armed with the right information you can make an informed decision to get the best quality and value for money. White diamonds are predominantly graded using four key factors - cut, clarity, carat and colour. All four are equally as important as one another and are fully accessible to customers if the diamonds have been certified by a diamond grading organisation like the Gemmological Institute of America (GIA). Today, we’re going to breakdown each of the four C’s and explain why you should have a comprehensive understanding of this before investing in your next piece of jewellery, whether it be an engagement ring or a dress piece.
Cut
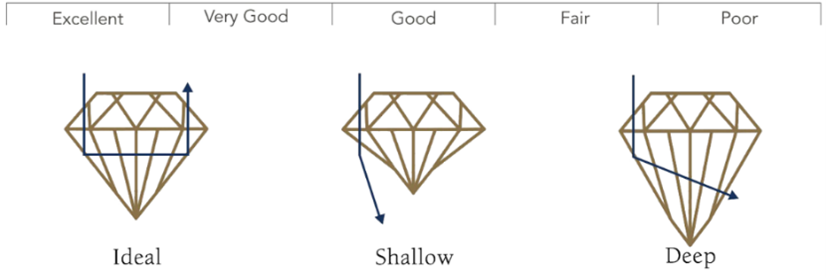
Put simply, cut is the way in which a diamond’s facets interact with light and refers to the polish, proportions and symmetry rather than the physical shape. For example, a brilliant cut diamond is round in shape, however its polish, proportions and symmetry are what make up the cut gradings and dictate the amount of fire, brilliancy and scintillation, otherwise known as sparkle. The rating scale ranges from excellent through to poor. At Hogans, every round brilliant diamond we source is triple excellent. This means that the cut proportion, polish and symmetry are optimal, allowing light to enter through the table and crown, then refract from the pavilion and back up through the table, travelling in a U-shape. If a diamond’s proportions are too shallow or deep, the light will be directed down through the bottom of the stone which drastically reduces sparkle. Our fancy shaped diamonds are also selected very stringently ensuring an optimum sparkle and ideal desired shape.
Expert tip: Always ask for triple excellent diamonds
Colour
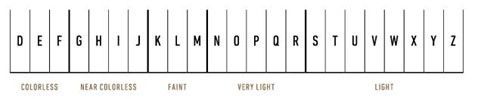
Diamonds are graded by colour on a scale from D and work all the way through to Z. D is completely colourless and as a general rule at Hogans, our white diamonds don’t drop below a H. Coloured diamonds have their own colour grading systems, however they are also graded under the same system across the other 3Cs.
Expert tip: Never go below a H in colour
Clarity
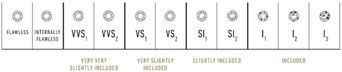
Clarity grading refers to the naturally occurring flaws in a diamond, much like a birthmark. These inclusions (internal) or blemishes (external) can be black or white in colour and characteristics can range from feather to crystal shaped masses under a microscope. GIA’s clarity scale is made up of 11 grades with flawless being optimal and included 3 being the poorest. Though a flawless diamond is most sought after, they are exceptionally rare and can increase the price/value of the stone by a considerable amount. Understandably the most common clarity that customers request is within the VS range.
Expert tip: Never go below an SI2 clarity grade
Carat
Diamonds and gemstones are weighed in metric carats with a one carat diamond being equal to 0.2 of a gram. A carat is divided into 100 points, so often you will hear jewellers or sales consultants refer to the weight by the number of points, for example a 0.50ct diamond is called a 50-pointer. The most important thing to remember when purchasing a diamond is that carat is only the weight so although you may compare three separate 1ct (or 100 point) diamonds, the price isn’t all based on weight. The quality is what will determine the value of the stone, therefore the clarity, colour and cut do impact the final price.
Expert tip: Never compare a diamond using carat versus carat.
That’s Not All
The 4C’s are paramount of course, but one other factor that is often overlooked is the fluorescence of a stone. Fluorescence refers to the amount of trace minerals that’ve been trapped in the stone at the time of its creation. Diamonds that have fluorescence will look milky, cloudy or even blue when exposed to sunlight, and therefore reduce the sparkle and lustre of a diamond. When procuring a diamond, always check that the stone has none or nil fluorescence. Hogans are very proud to stock stones that contain Nil or minimal traces of fluorescence, meaning your diamond will look amazing whether your indoors or outdoors in natural light.
Expert tip: Check that your diamond is certified and contains nil fluorescence
So how can you make sure you’re getting all of the right specifications about your diamond before making the purchase? We always recommend purchasing certified diamonds that have been laser inscribed with their individual certificate number. If it is a GIA certified diamond, the diamond will come with the corresponding report that looks like the sample above. If you’re unsure whether the report is legitimate, you can always ask the jeweller to place the diamond under a microscope to show you the laser inscription and check this against the report.
To book your a consultation with one of our expert diamond consultants, please visit this page and fill out the enquiry form.