When you purchase a piece of fine jewellery, you're investing in a legacy of craftsmanship, tradition, and authenticity. One of the most important yet often overlooked aspects of jewellery is the hallmark stamp, a tiny yet powerful symbol etched into the precious metal we use. In this journal, we explore the meaning behind hallmark stamps that can be found in jewellery, their significance, and why they are crucial for both jewellers and you, as our customers.
What is a Hallmark?
A hallmark is a mark or series of marks stamped on a piece of precious metal jewellery, serving as a guarantee of the metal's content and quality. Hallmarks have a long history, dating back to ancient times, but they were formally established in the United Kingdom during the 14th century. The purpose of hallmarking is to ensure that consumers are getting exactly what they pay for - genuine precious metal of a specified purity.


The History of Hallmarking
Hallmarking in the UK can be traced back to 1300 when King Edward I introduced legislation requiring all gold and silver items to be tested and marked by guardians of the craft. This early form of quality control laid the foundation for the hallmarking system we know today. The Worshipful Company of Goldsmiths, later known as The Goldsmiths' Company, was given the responsibility of testing and marking precious metals. This practice was designed to protect both the buyer and the reputation of the craft, ensuring that only metals of a certain standard were allowed to be sold.
Over the centuries, hallmarking has evolved, with additional marks being introduced to convey more information about the piece. Today, hallmarking is a legal requirement for most precious metal items sold in the UK, ensuring that customers receive a product that meets the highest standards of quality.
The Components of a Hallmark
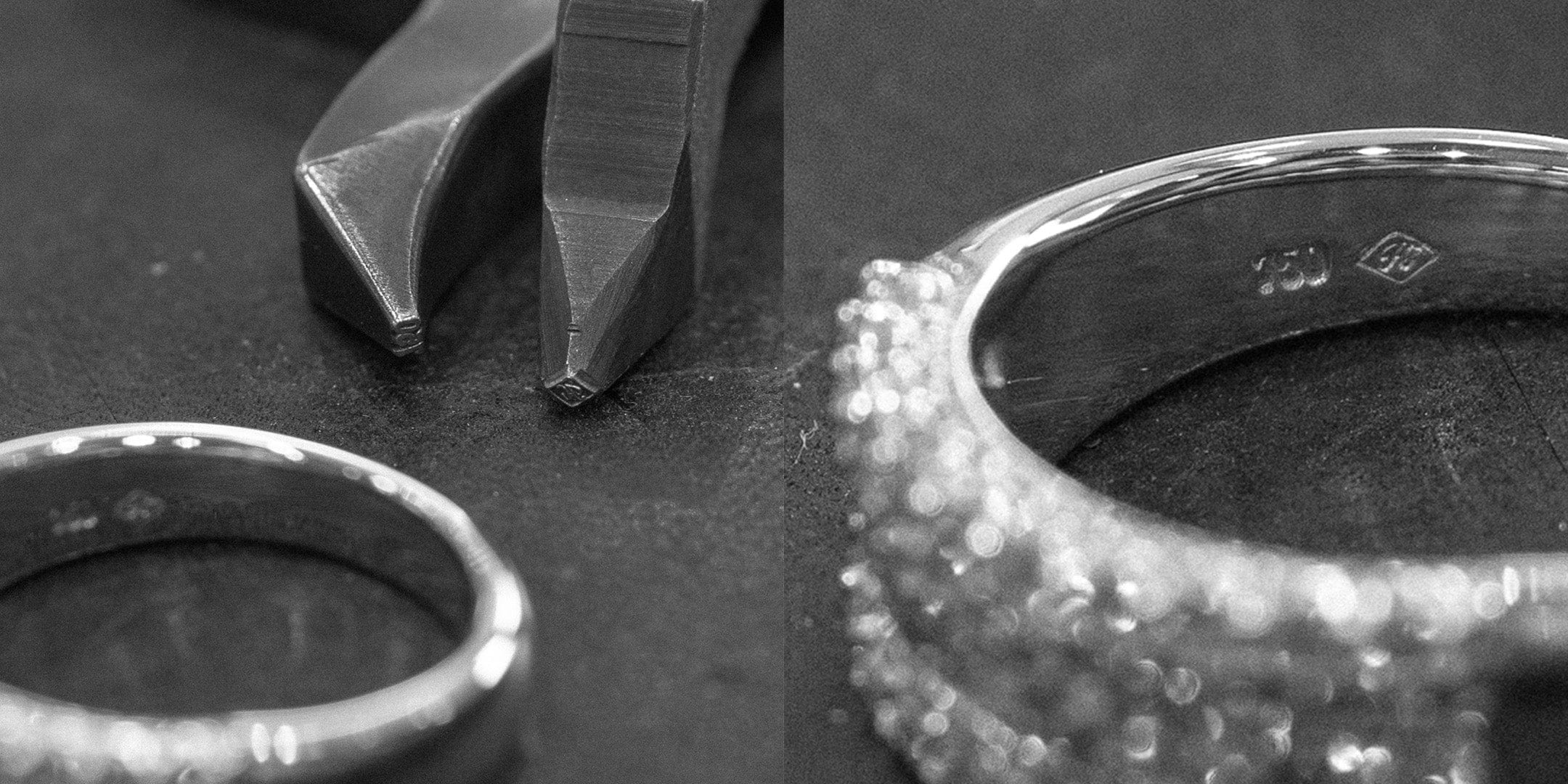
A hallmark typically consists of several components, each providing specific information about the piece of jewellery. These include:
1. Sponsor’s Mark: Also known as the maker’s mark, this is usually the initials of the person or company responsible for sending the item to be hallmarked. It identifies the origin of the piece.
2. Assay Office Mark: This mark indicates which assay office tested and marked the item. There are four assay offices in the UK: London, Birmingham, Sheffield, and Edinburgh. Each has its unique symbol—the leopard’s head for London, an anchor for Birmingham, a rose for Sheffield, and a castle for Edinburgh.
3. Metal and Purity Mark: This mark shows the type of metal and its fineness or purity. For gold, for example, the mark might be ‘375’ for 9-carat gold or ‘750’ for 18-carat gold. Silver is usually marked with ‘925’ for sterling silver, while platinum and palladium have their own specific marks.
4. Date Letter: While not always present on modern jewellery, the date letter is a mark that can help determine when the item was hallmarked. Each year has a corresponding letter, making it possible to trace the age of a piece.
5. Optional Marks: These can include commemorative marks, such as those applied during special events like the Queen’s Platinum Jubilee. They may also include additional purity marks or symbols indicating where the metal was sourced from, such as the Fairtrade mark.
The Importance of Hallmarking
For jewellers and customers alike, hallmarking is a crucial aspect of the jewellery trade. For the consumer, it provides peace of mind, knowing that the piece they are purchasing is genuine and meets the necessary standards of purity. This is particularly important when investing in high-value items such as engagement rings or heirloom pieces, where authenticity and quality are paramount.
For jewellers, hallmarking not only assures customers of the quality of their products but also protects the reputation of their craft. By adhering to the hallmarking system, jewellers demonstrate their commitment to quality and transparency, building trust with their clients.
Hallmarking in the Modern Era
In today's globalised market, hallmarking remains as important as ever. With the rise of online shopping and international trade, consumers are more vulnerable to purchasing counterfeit or substandard jewellery. Hallmarks act as a safeguard against these risks, providing a verifiable standard of quality.
The hallmarking process itself has also evolved with technology. Modern assay offices use a combination of traditional methods and advanced equipment, such as X-ray fluorescence (XRF) analysis, to test the metal's composition without damaging the piece. Once the metal has been tested and verified, the hallmark is applied using precision techniques, ensuring it is clear and legible.
When inspecting a hallmark, the key is to familiarise yourself with the various marks and their meanings. A good starting point is to identify the metal and purity mark, as this provides immediate information about the quality of the piece. From there, look for the assay office mark and the sponsor's mark, which can help trace the origin of the item. If there is a date letter, it can offer valuable insight into the piece's history.
Hallmark stamps are more than just tiny engravings on your jewellery - they are a testament to the piece's quality, authenticity, and craftsmanship. Understanding these marks can enhance your appreciation of your jewellery and provide assurance that your investment is well-founded. Whether you are a seasoned collector or a first-time buyer, the hallmark is your guarantee of the value and integrity of the jewellery you own.